The water footprint of hydrogen
Depending on how hydrogen is produced, there are three main types: gray, blue and green hydrogen.
Please contact us.
Types of hydrogen
Gray hydrogen
Gray hydrogen is produced from fossil raw materials using steam and methane (steam methane reforming). This gray hydrogen is widely used for ammonia synthesis in the production of fertilizer and for the refining of fossil fuels.
In the context of sustainable development of the industry, we are working hard on solutions to limit CO2 emissions. This can be partly achieved through the transition to blue hydrogen production.
Blue hydrogen
Blue hydrogen is produced in the same way from fossil raw materials and resources, but the CO2 released is stored or converted into, for example, methanol (CCUS = carbon capture utilization and storage).
The transition from gray to blue hydrogen is a step that can be made relatively quickly. However, due to limitations in the storage capacity for CO2 and the high energy consumption of this production method, it is expected that the industry will also partly switch to sustainable green hydrogen in the future.
Green hydrogen
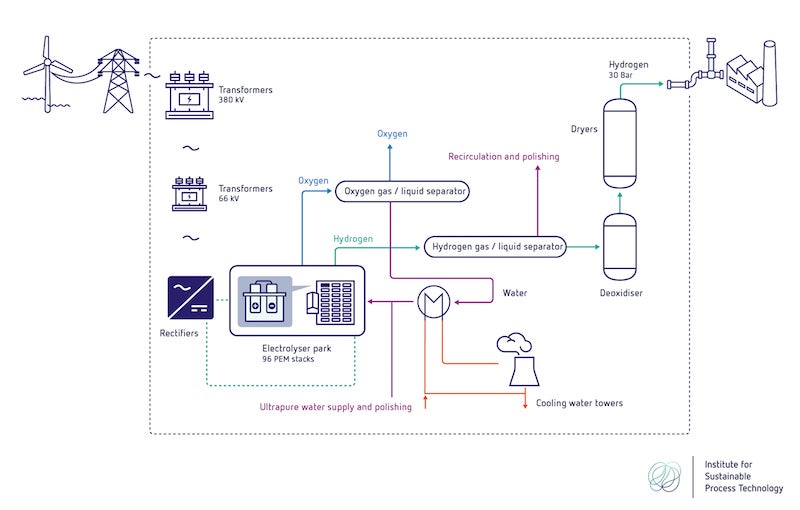
Green hydrogen is not produced from fossil raw materials. Only green energy is used to make the hydrogen, usually from wind or solar energy. Green hydrogen is widely seen as the essential fuel and raw material for sustainable development of the transport sector and industry.

Electrolyzers are used for the production of green hydrogen, which are supplied with green electricity and demineralized water. Furthermore, cooling water is sometimes used for the cooling of electrolyzers and compression of hydrogen.
Source: Creative Commons Attribution – No Derivatives License (CC BY-ND 4.0)